The Many Benefits of Mulching Your Garden Beds
Does your garden need a little boost? By mulching garden beds, you’ll be providing so many benefits to your outdoor spaces, including helping to promote plant health and optimize growing conditions.
Mulching is a technique that involves covering garden beds with a layer of organic or inorganic materials and which offers a variety of benefits to your garden.
From conserving moisture and controlling weeds to improving soil health and regulating temperature, mulching plays an important part in creating a flourishing garden space.
In this post, I’ll share the many benefits of mulching your garden. You’ll learn about the different types of mulch there is, and best practices in your garden.

As an Amazon affiliate, I earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you. My blog also features other affiliate links for your convenience. Click here to read my privacy policy.
Benefits of Mulch in Garden Beds
1. Control Weeds Naturally By Mulching Garden Beds

Mulching plays a crucial role in controlling weed growth in the garden.
It helps to suppress weed growth, reducing the need for excessive manual weeding of your flower beds, and minimizes the use of chemical herbicides throughout your garden.
A thick layer of mulch acts as a natural barrier, blocking sunlight and preventing weed seeds from germinating. This use of mulch reduces the weed competition for nutrients, water, and sunlight.
2. Moisture Conservation from Garden Bed Mulch

One of the primary benefits of mulching is its ability to conserve moisture in the garden soil.
By acting as a protective barrier, mulch reduces water evaporation from the soil surface, preventing water loss during the hot summer months.
Wood chips, grass clippings, pine needles, or dry straw are excellent organic mulch materials that can help retain soil moisture effectively.
3. Soil Erosion Prevention With Garden Bed Mulch
Mulch in garden beds can also help with preventing soil erosion, especially in sloped areas or regions of heavy rains. The layer of mulch acts as a protective shield, preventing rainwater from directly hitting the soil surface and washing away valuable topsoil.
This helps to maintain the integrity of your garden beds and ensures that essential nutrients stay in place, providing a fertile environment for healthy plant growth.
4. Nutrient Enrichment for Healthier Plant Growth

As organic mulch materials break down, they gradually release nutrients into the soil. This release acts as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil and providing a steady supply of essential elements for your plants.
Wood chips, lawn clippings, and dry straw are all very effective at enhancing soil fertility and growing healthy plants.
5. Soil Health Improvement When Mulch Gardening
Another advantage of mulching significantly contributes to soil health by adding organic matter to the garden soil and improving soil aeration, drainage, and the retention of soil nutrients.
6. Soil Temperature Regulation
Another benefit of mulching is its role in regulating soil temperature.
A blanket of mulch acts as a natural insulator, keeping the soil cooler during hot weather and protecting plant roots from freezing temperatures in colder climates.
This is the best way to create a more stable and healthy soil environment, extending the growing season and improving the resilience of your plants.
We mulch our fallen leaves in the autumn with the lawn mower and spread them throughout the flower beds to protect them from winter temperatures. This is added protection for those gardens in hardiness zones that can keep dahlia tubers in the ground through the winter.
7. Protect the Root Zone By Mulching
Mulching creates a protective layer around plant roots, shielding them from extreme temperatures, both hot and cold.
This insulation effect helps to maintain a stable soil temperature within the root zone, preventing stress and ensuring optimal plant growth. By keeping the soil cooler during hot weather, mulch also reduces the risk of water loss through evaporation, preserving soil moisture for the roots to access.
Types of Mulch
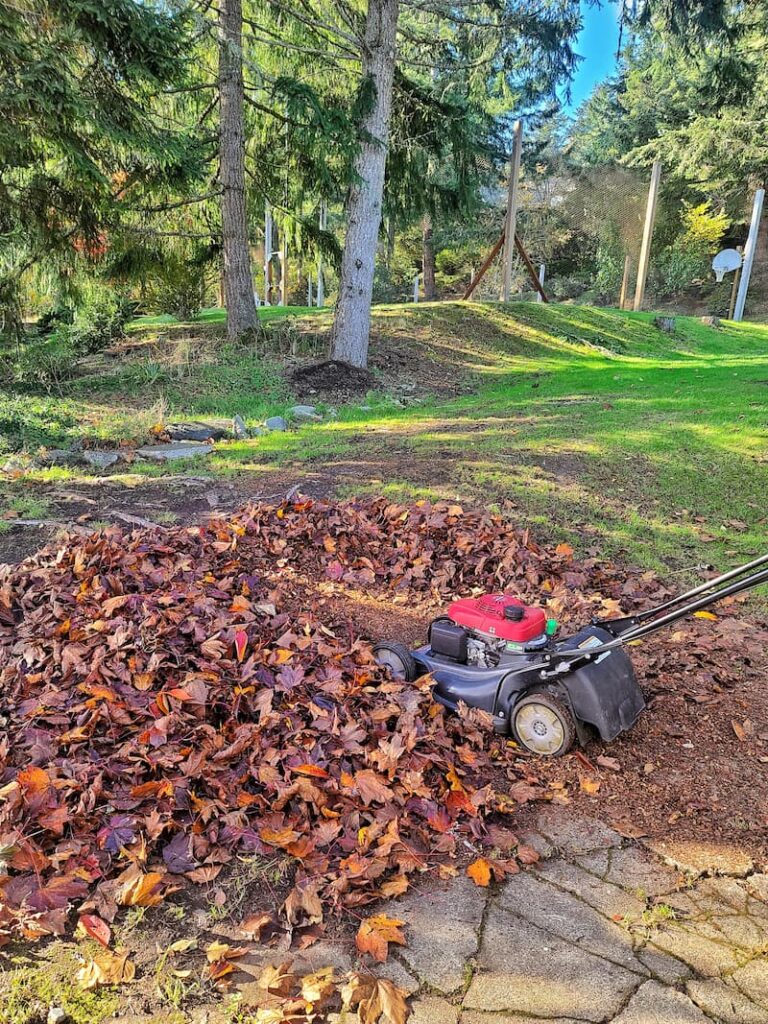

What is mulch made of? Mulch can be made of various organic or inorganic materials, depending on the desired purpose and aesthetic preferences. Here are some common types of mulch materials:
Organic Mulch
Inorganic Mulch
Although landscape fabric is not technically mulch, it is sometimes used as a barrier to suppress weeds when combined with another mulch layer.
When choosing from the different types of mulch for your garden beds, consider factors such as aesthetics, availability, and the specific needs of your plants.
Mulching Your Garden Can Be Simple and Cost-Effective

Mulching is a simple and cost-effective gardening practice that is relatively easy to apply and maintain.
Applying mulch is as simple as spreading a layer of the type of mulch you choose over the garden bed surface.
Organic mulch materials, such as wood chips or grass clippings can be found in your own yard or from local sources, making it an eco-friendly option.
Best Practices for Mulching

By following these best practices, your mulching efforts will result in healthier plants and a more beautiful garden.
Properly Apply and Avoiding Excessive Mulch
To achieve the best results in your garden, apply a thin layer (2-4 inches) of mulch. That amount will provide adequate coverage for weed suppression and moisture retention without suffocating plant roots.
Leaving Gaps Around Plant Stems and Tree Trunks
Leave a small gap around the base to allow air circulation and help prevent fungal diseases. By leaving a small space, you promote airflow and prevent issues.
Replenishing Mulch as It Decomposes
Replenish the mulch layer as it decomposes, typically yearly. Over time, organic mulch breaks down, contributing to soil fertility. Keep an eye on the mulch layer and add more as needed to maintain the desired thickness.
Mulching Around Flower Beds and Garden Borders
Focus on mulching around flower beds and garden borders. Applying mulch in these areas enhances the overall aesthetics, defines the garden’s structure, and helps keep weeds at bay.
Common Questions About Mulching in the Garden
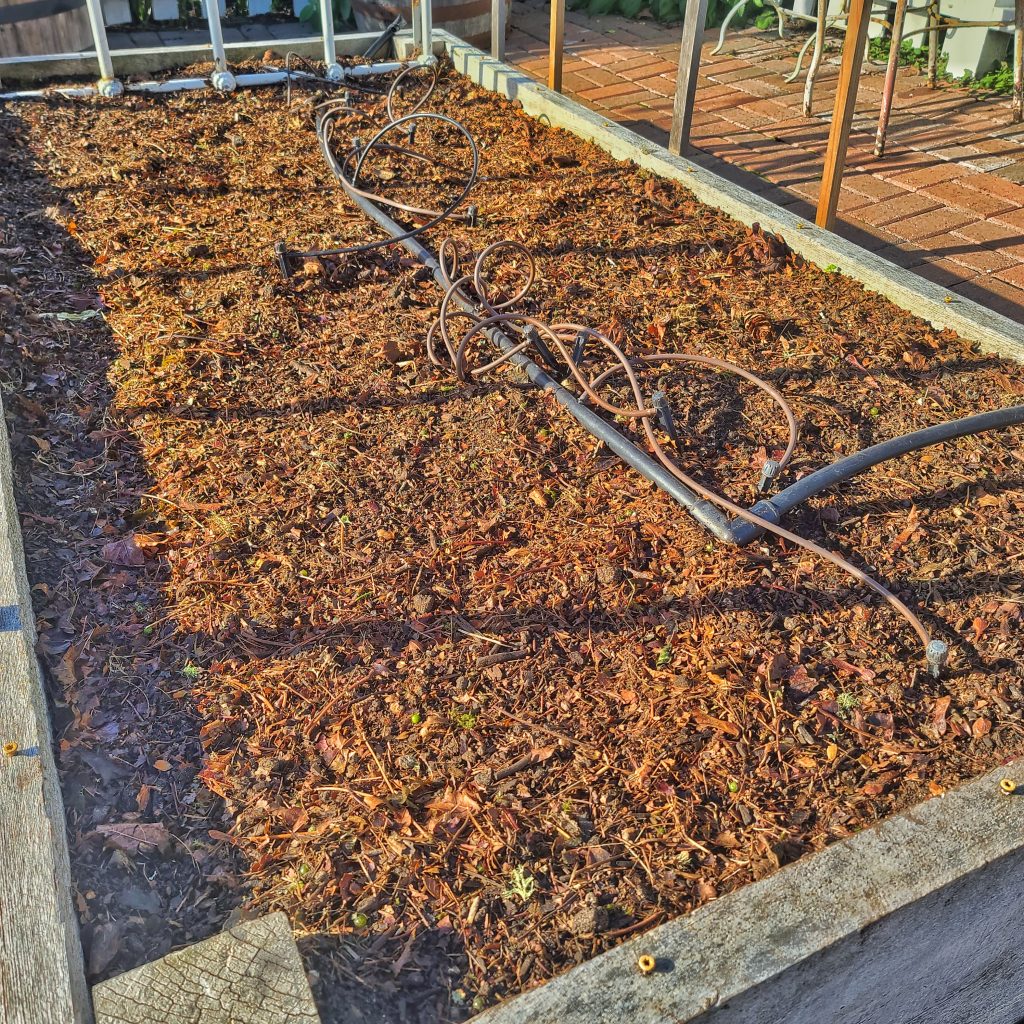

What Should I Put Down Before Mulching?
Before mulching your garden beds, prepare your soil and create the optimal foundation for the mulch.
Can you Explain the Process of Mulching With Cardboard?
Mulching with cardboard is an effective and environmentally friendly method that helps suppress weeds and improve soil health.
What are the Best Mulching Blades?
Is Decorative Bark Considered a Type of Mulch?
Yes, decorative bark is considered a type of mulch. It’s a popular choice for both functional and aesthetic purposes in gardening and landscaping.
Decorative bark mulch is typically derived from tree bark, and processed and prepared to use in garden beds and around plants.
What is the Best Mulch for Garden Beds?

The best garden mulch depends on many factors, including your specific gardening goals, plant preferences, local climate, and availability of materials. Refer to the “Types of Mulch” section earlier in the post for options.
What is the Best Leaf Mulcher?
Here are my top picks for 2023…
What is the Best Mulch for a Vegetable Garden?

Here are some options for mulch in a vegetable garden:
Consider the specific needs of your vegetable crops, local climate, and availability of materials when choosing the best mulch for your vegetable garden.
Final Thoughts
The use of mulch in your garden beds provides numerous benefits, including water retention, weed control, improved soil health, and soil temperature regulation.
Whether you choose organic materials like wood chips, grass clippings, or dry straw, or prefer inorganic options like stones or gravel, mulching is a good idea for promoting healthy plants and vibrant flower gardens.
If you have any questions or have a message, I’d love to hear from you. Leave a comment below. And be sure to share this blog post link with anyone who may find these gardening tips useful.
Until next time,
Happy Gardening!

I’m a self-taught hobby gardener. Everything I share on my blog is my opinion and what has worked for me.
Follow Me for More Inspiration
Shop my Amazon Storefront, LTK sources, and my favorite home decor, garden, and lifestyle products. When you purchase from one of my links, I earn a small commission, which helps me continue sharing all the content you expect on my blog.
Be sure to follow me on Pinterest, Instagram, Facebook, TikTok and LIKEtoKNOW.it. Do you like gardening? Join my Facebook Gardening Tips & Tricks group.









